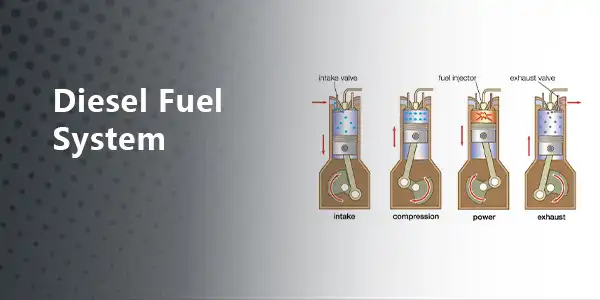
Components Of Diesel Fuel System
A diesel fuel system is an internal combustion engine that converts chemical reactions into mechanical energy. It uses a series of pistons to compress fuel and air before ignition. In a diesel engine, air is compressed and then injected with gasoline. When air is compressed, it heats up, and the compressed air ignites the gas. Since diesel engines are fueled after the air is compressed, they have better control over fuel utilization. In fact, these engines are considered one of the most fuel-efficient systems in construction machinery. Basic diesel fuel system components include the diesel fuel tank components, the fuel lines, the fuel filters, the fuel pumps, and the fuel injectors. This article focuses on the fuel tank, the fuel lines, and the fuel filter.
The Diesel Fuel Tank Components
A fuel tank is a container that stores fuel and helps to maintain the temperature of the fuel below the ignition point. The fuel tank also serves as an important means of cooling the fuel returning from the engine. The fuel tank should be corrosion-resistant, leak-free, and have a pressure of at least 30 kPa. It must also use some means to prevent excessive pressure build-up, such as a vent or safety valve. Fuel tanks can be divided into open fuel tanks and closed fuel tanks. The installation of the fuel tank of the diesel generator set is also exquisite. Different types of diesel generator sets have corresponding standard fuel tanks and fuel supply systems. There are many types of fuel tank designs, which can be designed into separate fuel tanks of various capacities according to user requirements.
The Fuel Lines
The layout of the engine fuel lines has an important impact on the diesel fuel system components performance and it provides insurance to the system. In addition, the diesel engine vibrates greatly during operation, and many parts of the main body are in a high-temperature state. The design of the fuel lines and the structural design of the joints on the oil supply and return pipelines should take into account the highest peak pressure that will appear when the pump and injector are working. Diesel vehicles have three different fuel lines. Heavy-duty fuel lines can withstand the high pressure between the fuel injection pump and injectors. The medium-weight fuel line is designed for moderate to light fuel pressures that exist between the fuel tank and the injection pump. Lightweight fuel lines can be used where there is little to no pressure.
The Fuel Filter
The fuel filter is connected in series on the lines between the fuel pump and the oil inlet of the throttle body. Its structure is composed of an aluminum shell and a bracket with stainless steel inside. The function of the fuel filter is to remove iron oxide, dust, and other solid impurities in the fuel to prevent the fuel system from clogging (especially the fuel injector), reduce mechanical wear, and ensure stable engine operation.
In conclusion, understanding the basic components of the fuel system in a diesel engine, including the fuel tank, fuel lines, and fuel filter, is important to maintaining the efficiency of your diesel engine. Proper care and maintenance of these diesel engine fuel system components ensures that the diesel engine continues to operate at its best, making it a reliable choice for construction machinery. By understanding the complexities of the diesel fuel system, we can harness the power of the internal combustion engine while maximizing fuel efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
 Track Your Order
Track Your Order