Four Major Components of An Alternator
An alternator VS a generator
First of all, we need to figure out that what’s the difference between an alternator and a generator. By definition, the biggest difference between them is the conversion of mechanical energy. An alternator is a device that converts mechanical energy into AC electrical energy, while a generator is a mechanical device that converts mechanical energy to either AC or DC electrical energy.
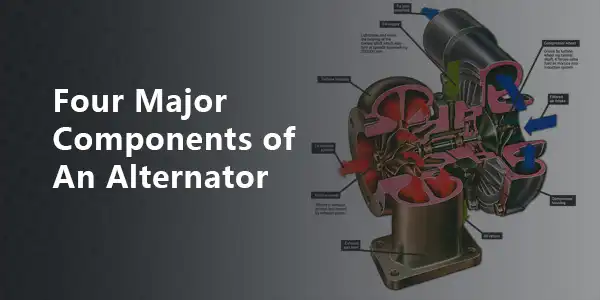
Four major components of an alternator
Undoubtedly there are many different alternator types, so their construction is different. The four major components of an alternator: the rotor, the stator, the rectifier, and the voltage regulator. Here we will introduce these components in details.
The rotor
One of the components of an alternator is rotor. The rotor is also known as the rotating magnetic core, or the engine flywheel of the alternator. The rotors are the moving parts of an alternator, which has permanent magnets. The rotor creates a moving magnetic field around the stator which creates a voltage difference between the windings of the stator which produces the alternator's AC output.
The stator
The stator is the stationary components of an alternator and consists of three separate coil windings, each connected together at one end. There is a brush and a slip ring at each end of the stator shaft. The stator coil windings are evenly spaced at 120-degree intervals around the iron shaft. If the coil is stationary, like in the stator, if you move the magnetic field across the coil, you get a voltage induced in the coil, the faster the magnetic field changes, the more voltage is generated. Due to the rotating magnetic field, the rotating rotor inside the stator induces voltages on the stator windings.
The rectifier
The rectifier consists of several diodes. Diodes only allow current to flow in one direction. A diode has two terminals, an anode and a cathode. If the anode is more positive than the cathode, current will flow through the diode. But if the anode is more negative than the cathode, current will not flow through the diode. Alternator rectifiers have more than one diode. Typically, alternator rectifiers have six diodes. The six diodes are housed in a heat sink material to protect them from burning out.
The voltage regulator
Voltage regulators come in a variety of shapes and sizes, depending on the supplier and the model of alternator. The function of the voltage regulator is to adjust the excitation voltage of the electromagnet so that the stator output voltage remains relatively constant without being affected by the rotor speed.
How does these four major components work together?
First, please keep in mind that above mentioned information might not exactly match your alternator as there are different configurations of alternators.
The ignition switch allows the battery to charge the rotors. As the engine speed rises, the rotors spin faster. When the stator voltage increases, the rectifier output battery charging voltage increases, and the voltage regulator detects the increase in battery voltage. The voltage regulator reduces the electromagnet energization voltage, and the stator voltage drops.
 Track Your Order
Track Your Order