Working Principle Of Alternator
1. The working principle of the forklift alternator
The alternator is driven by the engine, and its function is to supply power to the electrical equipment when the forklift engine is working normally and to charge the forklift battery.
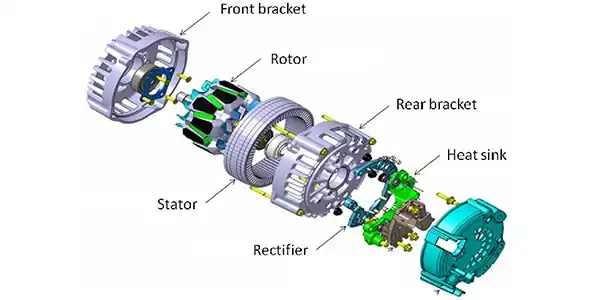
(1) Power generation principle: The alternator is made of the electromagnetic phenomenon that the coil located in the alternating magnetic field generates induced electromotive force. When the rotor winding has a current passing through it, N and S poles are formed. When the rotor rotates, the alternating magnetic field generates an induced electromotive force in the stator winding. Because the three-phase stator windings are symmetrically arranged on the same iron core, the phase difference is 120 degrees, so the symmetry is obtained. from a three-phase alternating current.
(2) Rectification principle: The three-phase alternating current of the forklift generator is rectified by three silicon diodes, and the cathodes of the three diodes (VD1, VD3, VD5) are connected in the three-phase bridge rectifier circuit to form the generator output direct current the positive pole. During the rectification process, the diode with the highest positive potential is turned on, and the anodes of the three diodes (VD2, VD4, VD6) are connected to form the negative pole of the DC output of the forklift generator parts. During rectification, the diode with the lowest negative potential is turned on. After rectification, a relatively stable DC pulsating voltage is obtained on the load.
(3) Magnetic field winding current circuit. When the alternator rotates at a low speed and the generator voltage is lower than the voltage of the forklift battery, the forklift battery supplies the magnetic field winding current through the ignition switch to perform separate excitation to enhance the magnetic field, so that the forklift generator voltage is very fast rise. When the forklift generator speed increases and the voltage is higher than the forklift battery voltage, the generator changes from separate excitation to self-excitation.
2. Charge fault phenomenon:
When the engine runs above medium speed, the ammeter indicates discharge, and the charging indicator light does not go out. Measure the generator terminal voltage as the battery voltage.
(1) Analysis of the reasons why the alternator does not charge:
1) The generator belt is broken or slipped seriously;
2) The generator excitation circuit or charging circuit is an open circuit;
3) Generator failure: poor contact between brushes and slip rings; diode breakdown, open circuit; rotor winding short circuit, open circuit or grounding; stator winding short circuit, open circuit, grounding;
4) Regulator failure: insufficient spring elasticity, too small air gap, high-speed electric shock sintering, contact ablation, and dirt while adjusting the resistance section; the regulator tube and low-power triode of the transistor regulator are short-circuited or open to the power triode; adjust The grounding method of the generator does not match the generator.
(3) The steps of the fault diagnosis method for the alternator not charging
1) Check the belt tightness and wire connection (loose or wrong connection) in turn. If normal, go to the next step.
2) Check the excitation circuit
Carry out the electromagnetic suction test on the generator, if it is not normal, check the excitation circuit. It should first be distinguished whether it is the fault of the generator or the fault of the regulator (power on the rotor winding of the generator, and prove it by testing whether it has electromagnetic attraction). If normal, go to the next step.
Check the armature circuit (use a test lamp to check whether the generator "B" terminal has the power to determine whether the fault is on the external circuit or inside the generator.
Our website also provides cooling engine fan 30102058, you can buy a variety of spare parts for excavators, and aerial platforms on our website.
In conclusion, the alternator in a forklift plays an important role in generating electricity, providing energy to various components, and charging the forklift battery. The working principle of an alternator relies on the electromagnetic phenomenon in the alternating magnetic field, which results in the generation of induced electromotive force in the stator winding. The principle of an alternator is to convert three-phase alternating current into relatively stable direct current through rectification for use in the power system. The alternator charging principle involves the complex interaction of field winding current circuits. As the alternator speed increases, there is a transition from separate excitation to self-excitation.
 Track Your Order
Track Your Order